1. Overview & Common UI
The AVE II User Interface is built upon Unreal Engine’s Common UI Plugin.
Common UI is a framework designed to handle complex widget hierarchies and layer management. In this project, we utilize it primarily to standardize our widget base classes and manage the activation states of our UI layers.
- Base Class: Most UI elements in the project inherit from
CommonUserWidget. - Documentation: For a deep dive into the underlying plugin, please check Unreal Engine’s Common UI Documentation.
⚠️ Important: Please make sure the Common UI plugin is enabled. If it is disabled, you will encounter Blueprint compilation errors throughout the project.
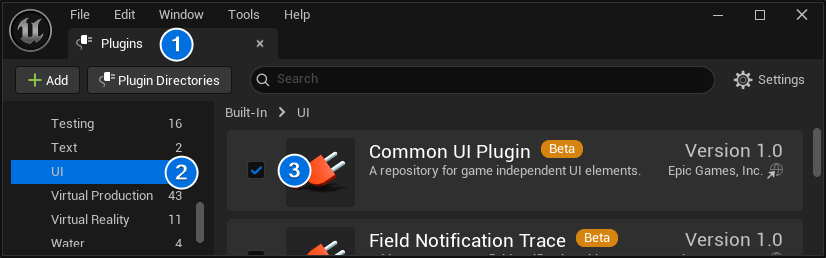
To enable the plugin, navigate to: Edit > Plugins > Built-In (left scroll menu) > UI > Common UI Plugin (check “Enabled”).
2. Input & Navigation Logic
Common UI is often used for complex gamepad navigation trees (“Input Routing”). On the other hand, AVE II is a mouse, keyboard, and touch-centric visualization tool. Therefore:
- Navigation: We do not utilize the controller-based “Navigating Menus” or complex input routing features.
- Activatable Widgets: We do extensively use the Activatable Widget functionality. This allows us to cleanly activate and deactivate specific UI containers (like the Game Menu), ensuring they are properly registered by the system.
3. Architecture
The UI hierarchy is structured around a central stack that manages the transition between application states.
The Master Stack (WBP_Master_Stack)
📂 Location: AVEII > UI > Menus
The root of the user interface is handled by the WBP_Master_Stack.
- Initialization: This stack is created and added to the viewport directly by the Player Controller (BP_AVE_PC).
- Flow: Its primary role is to push the
WBP_Startup_Menu. Once the intro sequence ends, the Player Controller triggers the stack to Activate the main workspace:WBP_Game_Menu.
The Primary Workspace (WBP_Game_Menu)
📂 Location: AVEII > UI > Menus
The WBP_Game_Menu acts as the central hub where the user spends the majority of their time. Unlike a traditional game HUD, this serves as the main application window, containing the toolsets and panels required for real-time visualization.
For a detailed breakdown of the workspace layout and panel logic, please visit the Game Menu (WBP_Game_Menu) page.
4. Visual Style & Material Inheritance
Following the design patterns established by the Lyra example project, AVE II minimizes the use of static textures in favor of Material-based UI.
- Dynamic Styling & Animation: UI elements utilize dynamic materials rather than static images. This allows us to animate borders, as well as hover and selection states of buttons, directly within the material shader. The result is a fluid and dynamic user experience that feels alive and responsive.
- Inheritance: These materials are designed to inherit design parameters (such as color, opacity, and roughness) from their parent widgets. This creates a hierarchy where global style changes propagate automatically to child elements.